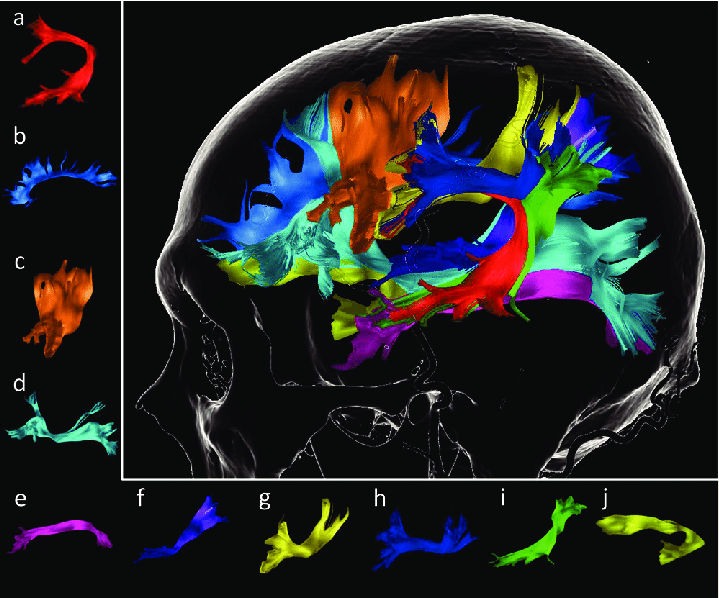
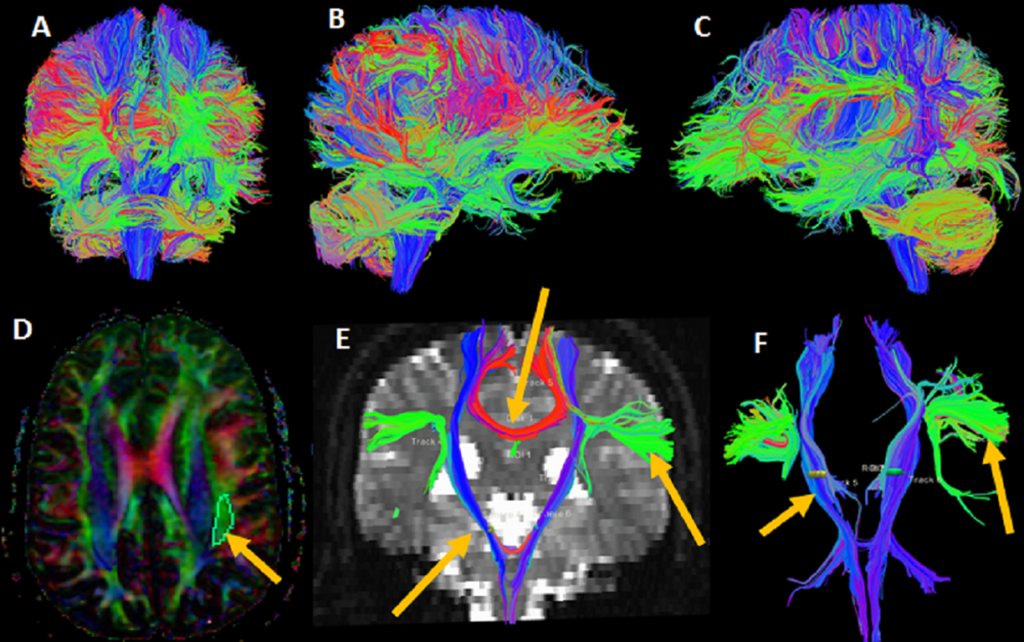
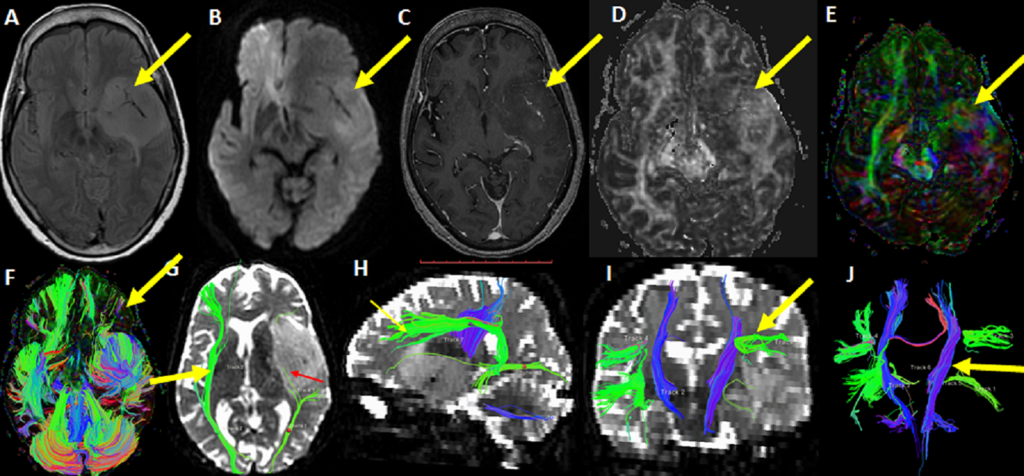
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), an MRI-based approach, uses water diffusion in neural tissue to map out white matter tracts in the brain. Tractography is a technique that has been widely used in clinical neuroscience to investigate the structure and health of the nervous system. Tractography has more recently been used in functional neurosurgery to help in neurosurgical targeting.
Water molecules move randomly due to diffusion, which is caused by their quick movement and numerous collisions with nearby molecules and structures [4]. Brownian motion is the name for this random movement of a suspended fluid without a mechanical or chemical gradient. The diffusion movements of water molecules along any axis follow a Gaussian distribution, assuming there are no nearby barriers.
How does tractography work?
The applied magnetic field is not uniform in the x, y, or z axes during diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (dwMRI). Depending on the field’s strength, this single-axis heterogenic “dephasing” field causes water molecules to move in a variety of ways. A non-uniform “rephasing” magnetic field is applied in precisely the opposite manner after a brief time gap (usually 10–100 ms).
The final MRI signal should be uniform from start to finish if water molecules are in exactly the same places in the applied gradient at the times of rephasing and dephasing. The signal will, however, be quantifiably diminished if water molecules move during the interval between these two time points.
Also Read: Apple launches e-sim in iPhone 14 series, check details:
A three-dimensional gradient in each of the x, y, and z axes is commonly used to acquire dwMRI. This enables the calculation of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of water in the brain, which measures the flux of these molecules under equilibrium conditions. However, the diffusion anisotropy, a characteristic that varies the volume of water diffusing in various directions, is not taken into consideration by this model.
Water mobility is constrained in one or more directions as a result of tissue architecture, which can be either normal or pathologic. Particularly, anisotropic diffusion of water occurs in tissues with highly structured tissue architecture and in tissues of specific types (such as axon membranes and microtubules). It makes sense that when the applied gradient is oriented in the same direction as the main direction of water diffusion, the signal attenuation will be at its greatest.
What is the primary feature of DTI and tractography?
The quantitative nature of DTI is among its most helpful characteristics. The white matter architecture of an individual or a group of individuals in particular brain regions can be compared using just a few summary numbers (e.g., before and after a surgical procedure). The mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy are the values that are most frequently employed in clinical research (FA).
Independent of anisotropy or direction, the diffusion tensor’s average size is represented by MD, the average of the eigenvalues. FA is a measure of the tensor shape that is independent of size or orientation. It summarises the level of anisotropy in a specific voxel. These numbers could change if there is neurological disease present, including cell death.
How many types of tractography are present?
In general, deterministic and probabilistic tractography methods are used often in clinical and scientific settings. The primary eigenvector of diffusion, as determined by the tensor at each voxel, the user-specified thresholds that limit the tract’s course, and user-specified seed points are used in deterministic tractography to compute white matter tracts.
The user-selected voxels of interest known as “seed points” are those through which the intended tract is thought to pass. Users can designate one or more seeds that are commonly referred to as “start points,” “mid points,” and “end points” and are known to be physically connected to the tract of interest. The local primary eigenvector field will then be followed from the initial seed point to the next adjacent seed point, forming a bidirectional streamline.
Even though the deterministic tractography uses a simplified methodology, it is rarely possible to estimate the orientation at every voxel with complete accuracy. A deterministic approach views the mean of the possible orientations for each voxel as the “actual” orientation. This mean is accompanied by a standard error, and these errors spread across the tract. As a result, there may be a lot of uncertainty in the white matter trajectory.
Also Read: Pakistan disowns JeM leadership and Masoor Azad for FATF relief
Probabilistic tractographic techniques take into account the whole distribution of potential orientations in all voxels coming from the given seed point rather than just the orientation of the dominant eigenvector. Deterministic tractography employs an orientation based on the mean of this distribution. The accompanying uncertainty is inversely correlated with the width of the distribution.
Following the computation of the number of tracts crossing each voxel, a probability map is created, and the voxels with the greatest number of tracts crossing them are added to the elongating streamline. The results of probabilistic tractography are more complex and reliable than those of deterministic tractography, but they are also more computationally intensive, more difficult to produce, and less understandable to comprehend.
Despite the fact that probabilistic tractography is praised for accounting for the uncertainty in diffusion imaging data, it has drawn criticism for being vulnerable to minute changes in data noise. As an alternative to deterministic and probabilistic techniques, global tractography was created with the goal of enhancing the reliability of fibre tracking with diffusion imaging.
With this method, the fiber arrangement that best describes the dwMRI data will be built. The local fiber orientation of an ambiguous voxel is defined by global tractography by analyzing the predicted orientations in the voxel’s spatial neighborhood, which is based on the idea that axons typically run in gently bending ordered fascicles.
Why is tractography significant in medical science?
There is a widespread belief that tractography could improve patient treatment accuracy. In a number of recent applications, mapping tracts that may be crucial for the effectiveness and side effects of DBS has been investigated.
Also Read: 9/11 attacks: Biden honors war victims in somber ceremony
The dentato-rubro-thalamic tract (DRT), which cannot be seen with conventional magnetic resonance imaging, is another fiber bundle that can be identified as an ideal DBS target. Tremor and treatment-resistant depression are two illnesses for which tractography has been suggested to improve clinical outcomes (TRD).
- Tremor Disorder
The most common movement problem in adults is essential tremor. Bilateral postural or kinetic tremor is how it manifests, and it can significantly lower quality of life. For the safe treatment of refractory essential tremor (ET) and other types of tremors, DBS is a viable option. DBS leads have been successfully stereotactically implanted in the ventral intermediate nucleus (Vim) of the thalamus by neurosurgeons.
Tractography results have led to the notion that manipulation of this tract may be significant for the effects of stimulation, especially in light of the proximity of the DBS electrodes to the DRT in patients who were successfully treated for tremor. This hypothesis has been tested in open label clinical studies with tractography as the targeting method and in a group of patients who were thought to be non-responders but who responded well to DBS when electrodes were re-implanted close to the DRT.
- Resistant Depression
DBS is being researched as a potential treatment for psychiatric problems, particularly the management of resistant depression, as a result of its effectiveness and safety in treating movement disorders. DBS has demonstrated promising benefits in early open label clinical trials when given to locations including the subequal cingulate gyrus (SCG), ventral capulse/ventral striatum (VC/VS), and others.
Researchers used bilateral targeting of the supero-lateral branch of the medial forebrain bundle (slMFB) in a series of trials using tractography-based DBS in TRD. The procedure’s justification was based on imaging tests done on people with Parkinson’s disease who were getting surgical treatment.
Dysphoria and mania may be brought on by DBS supplied through electrodes placed medially in the subthalamic area [52,53]. Inadvertent stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle (MFB) has been suggested as a potential anatomical substrate involved in these reactions. The authors’ tractography study revealed a midbrain tract that split into inferomedial and superolateral branches.
Conclusion
Numerous uses for tractography have been suggested as a result of expanding understanding of the significance of fiber routes for DBS surgery. Despite the tremendous developments, tractography has drawbacks when applied as is. Tractography, for example, cannot distinguish between afferent and efferent fiber tracts.
Despite these drawbacks, tractography-based DBS is a viable alternative to conventional DBS. Our understanding of the function white matter plays in disease pathology has greatly benefited from its contribution; for instance, the MFB has grown to be a focus of attention in the field of depression.
Also Read: Queen Elizabeth II: UK to observe a minute’s silence as mourning in the funeral
Researchers and clinicians may be better able to comprehend the pathophysiology of mood disorders if they use tractography techniques to improve DBS. The involvement of white matter is only briefly mentioned in many articles that concentrate on targetable brain areas that may contribute to depression.
However, the significance of fiber tracts is becoming more widely acknowledged as a significant element in depression as a result of the growing interest in connectomes and the Human Connectome Project. In order to treat these difficult psychiatric illnesses, neurosurgeons will presumably use tractography more frequently.